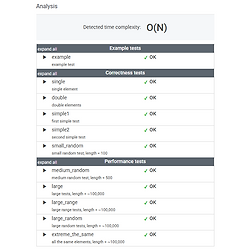
 Lesson 15. Caterpillar method - CountDistinctSlices #2 (속도 개선)
1. 속도 개선 아이디어이전 코드에서는 모든걸 하나하나씩 세고 있다. 예제를 다시 보면, A[0]A[1]A[2]A[3]A[4]34552 (0, 0) = 3(0, 1) = 3, 4(0, 2) = 3, 4, 5(1, 1) = 4(1, 2) = 4, 5... 이하 생략 ... 이전 코드에서는 첫번째 반복에서 (3), (3, 4), (3, 4, 5)를 세고,두번째 반복에서 (4), (4, 5)를 다시 세고 있다. 사실 처음에 계산한 slice에서 맨 앞 숫자인 3만을 제외하면, 두번째 반복에서 얻어지는 slice를 구할 수 있다.즉, 두번째 반복에서 처음부터 다시 세는것이 아니라, 그냥 3만을 제외하면, 두번째 반복에서 얻을 수 있는 slice를 모두 구할 수 있다. 2. 문제풀이 전략첫번째 반복문에서 3개를..
Lesson 15. Caterpillar method - CountDistinctSlices #2 (속도 개선)
1. 속도 개선 아이디어이전 코드에서는 모든걸 하나하나씩 세고 있다. 예제를 다시 보면, A[0]A[1]A[2]A[3]A[4]34552 (0, 0) = 3(0, 1) = 3, 4(0, 2) = 3, 4, 5(1, 1) = 4(1, 2) = 4, 5... 이하 생략 ... 이전 코드에서는 첫번째 반복에서 (3), (3, 4), (3, 4, 5)를 세고,두번째 반복에서 (4), (4, 5)를 다시 세고 있다. 사실 처음에 계산한 slice에서 맨 앞 숫자인 3만을 제외하면, 두번째 반복에서 얻어지는 slice를 구할 수 있다.즉, 두번째 반복에서 처음부터 다시 세는것이 아니라, 그냥 3만을 제외하면, 두번째 반복에서 얻을 수 있는 slice를 모두 구할 수 있다. 2. 문제풀이 전략첫번째 반복문에서 3개를..
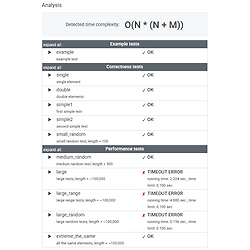 Lesson 15. Caterpillar method - CountDistinctSlices #1
1. 문제An integer M and a non-empty array A consisting of N non-negative integers are given. All integers in array A are less than or equal to M.A pair of integers (P, Q), such that 0 ≤ P ≤ Q For example, consider integer M = 6 and array A such that:A[0] = 3 A[1] = 4 A[2] = 5 A[3] = 5 A[4] = 2There are exactly nine distinct slices: (0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4) and..
Lesson 15. Caterpillar method - CountDistinctSlices #1
1. 문제An integer M and a non-empty array A consisting of N non-negative integers are given. All integers in array A are less than or equal to M.A pair of integers (P, Q), such that 0 ≤ P ≤ Q For example, consider integer M = 6 and array A such that:A[0] = 3 A[1] = 4 A[2] = 5 A[3] = 5 A[4] = 2There are exactly nine distinct slices: (0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4) and..
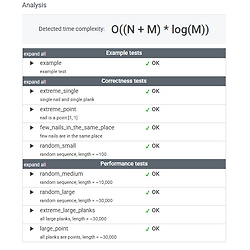 Lesson 14. Binary search algorithm - NailingPlanks #4 (속도 개선)
1. 속도 개선 아이디어이진 탐색 대상을 바꿔보자. AS_IS: 어떤 판자에다가 못질을 할까?TO_BE: 몇 번째 못을 사용하면, 모든 판자에 못질이 될까? 그런데 못은 순서대로 사용해야 한다. 따라서 이진 탐색으로 3번째 못을 골랐다면, 1, 2번째 못을 사용해야한다.이러면, 1번째, 2번째, 3번째, 순차적으로 못질하는 것과 같지 않을까? 이를 해결하기 위해선, 이번에도 생각의 전환이 필요하다.못을 들고, 판자에다가 하나하나 박을게 아니라, 현재까지 사용된 못 상태를 놓고, 판자를 못 상태에 대조하는 형태로 가야한다. 예시)C[0]C[1]C[2]C[3]C[4]467102 이를 배열로 표현해보면 다음과 같다.12345678910 못 못 못못 못 C[0] 못을 골랐다고 생각해보자.못의 상태 배열은 ..
Lesson 14. Binary search algorithm - NailingPlanks #4 (속도 개선)
1. 속도 개선 아이디어이진 탐색 대상을 바꿔보자. AS_IS: 어떤 판자에다가 못질을 할까?TO_BE: 몇 번째 못을 사용하면, 모든 판자에 못질이 될까? 그런데 못은 순서대로 사용해야 한다. 따라서 이진 탐색으로 3번째 못을 골랐다면, 1, 2번째 못을 사용해야한다.이러면, 1번째, 2번째, 3번째, 순차적으로 못질하는 것과 같지 않을까? 이를 해결하기 위해선, 이번에도 생각의 전환이 필요하다.못을 들고, 판자에다가 하나하나 박을게 아니라, 현재까지 사용된 못 상태를 놓고, 판자를 못 상태에 대조하는 형태로 가야한다. 예시)C[0]C[1]C[2]C[3]C[4]467102 이를 배열로 표현해보면 다음과 같다.12345678910 못 못 못못 못 C[0] 못을 골랐다고 생각해보자.못의 상태 배열은 ..