1. 문제
You are given integers K, M and a non-empty array A consisting of N integers. Every element of the array is not greater than M.
You should divide this array into K blocks of consecutive elements. The size of the block is any integer between 0 and N. Every element of the array should belong to some block.
The sum of the block from X to Y equals A[X] + A[X + 1] + ... + A[Y]. The sum of empty block equals 0.
The large sum is the maximal sum of any block.
For example, you are given integers K = 3, M = 5 and array A such that:
A[0] = 2
A[1] = 1
A[2] = 5
A[3] = 1
A[4] = 2
A[5] = 2
A[6] = 2
The array can be divided, for example, into the following blocks:
[2, 1, 5, 1, 2, 2, 2], [], [] with a large sum of 15;
[2], [1, 5, 1, 2], [2, 2] with a large sum of 9;
[2, 1, 5], [], [1, 2, 2, 2] with a large sum of 8;
[2, 1], [5, 1], [2, 2, 2] with a large sum of 6.
The goal is to minimize the large sum. In the above example, 6 is the minimal large sum.
Write a function:
int solution(int K, int M, vector<int> &A);
that, given integers K, M and a non-empty array A consisting of N integers, returns the minimal large sum.
For example, given K = 3, M = 5 and array A such that:
A[0] = 2
A[1] = 1
A[2] = 5
A[3] = 1
A[4] = 2
A[5] = 2
A[6] = 2
the function should return 6, as explained above.
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
- N and K are integers within the range [1..100,000];
- M is an integer within the range [0..10,000];
- each element of array A is an integer within the range [0..M].
주어진 배열을 K개의 블록으로 나눌 때, 각 블록의 합이 가장 큰 값(large sum)을 구한다. · · · · · · · · · · ①
①을 만족하는 값(large sum) 중 가장 작은 값(minimum large sum)을 찾는 문제.
M은 배열의 요소가 가질 수 있는 최대 값을 의미한다.
예시) K = 3, M = 5, return 6
| A[0] | A[1] | A[2] | A[3] | A[4] | A[5] | A[6] |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
배열을 3개의 블록으로 나눈다.
[2, 1, 5, 1, 2, 2, 2], [], [] → 각 블록의 최대 합 = 15
[2], [1, 5, 1, 2] [2, 2] → 각 블록의 최대 합 = 9
[2, 1, 5], [], [1, 2, 2, 2] → 각 블록의 최대 합 = 8
[2, 1], [5, 1], [2, 2, 2] → 각 블록의 최대 합 = 6
각 블록의 최대 합 중, 가장 작은 값을 반환한다.(return 6)
2. 매개변수 조건
- Vector A 크기 : 1 ~ 100,000
- K 값의 범위 : 1 ~ 100,00
- M값의 범위 : 0 ~ 10,000
- Vector A 요소 값의 범위 : 0 ~ M
3. 예제 분석
K값과 A의 크기에 따른 경우의 수를 생각해보자.
K \( = \) 1 경우,
블록이 1개이므로, A의 모든 요소값을 더해서 돌려주면 된다.
K \( \geq \) A.size 경우,
공집합을 활용할 수 있으므로, A의 요소를 1개씩 모두 자를 수 있다.
따라서 A의 요소 중 최대 값을 돌려주면 된다.
K \( < \) A.size 경우,
최소 2개 이상의 A 요소가 묶이게 된다.
즉, 여러가지 블록을 만들어서 large sum과 minimum large sum을 확인해야 한다.
여기서 주의해야 할 점은,
A가 K개의 블록으로 딱 나누어 떨어지지 않더라도, 공집합을 붙여서 K개의 블록으로 만들 수 있다는 사실이다.
4. 문제풀이 전략
minimum large sum은 블록을 어떻게 나누는지에 따라 달라진다.
A가 만들 수 있는 가장 작은 minimum large sum은 각 요소를 1개씩 나누는 것이다.
[2], [1], [5], [1], [2], [2], [2] → minimum large sum = 5 · · · · · · · · · · ②
반면, A가 만들 수 있는 가장 큰 minimum large sum은 1개의 블록으로 만드는 것이다.
[2, 1, 5, 1, 2, 2, 2] → minimum large sum = 15 · · · · · · · · · · ③
문제에서 구하고자 하는 값(X)은 ②와 ③, 저 사이에 있는 어떤 값이다.
즉, X를 기준으로 블록을 만들면 된다. (\( ② \leq X \geq ③ \))
여기서 포인트는 '블록을 나눌 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 탐색하는 것이 아니다'라는 점이다.
블록을 만드는 기준은 X이고, 그 때 만들어지는 minimum large sum을 찾으면 된다.
탐색하는 범위가 (\( ② \leq X \geq ③ \))로 정해져 있다는 것이 포인트이다.
5. 코드 (C++)
X값을 찾기 위해, 이진 탐색 알고리즘을 사용했다.
/**
* 블록을 만들고, 최대값을 찾는다.
* mid: block을 만드는 기준 값
* large_sum: 가장 큰 block 값
*/
int GetBlocks(int mid, int& large_sum, vector<int>& A)
{
int sum = A[0];
int blocks = 0;
for(size_t i = 1; i < A.size(); i++)
{
if(sum + A[i] <= mid)
{
sum += A[i];
}
else
{
if(sum > large_sum) large_sum = sum;
blocks++;
sum = A[i];
}
}
if(sum <= mid) blocks++;
return blocks;
}
int solution(int K, int M, vector<int> &A) {
int max_element = 0;
int total = 0;
//A 요소 합 구하기
//A 요소 중 최대값 구하기
for(size_t i = 0; i < A.size(); i++)
{
total += A[i];
if(max_element < A[i]) max_element = A[i];
}
//minimum large sum 찾기
if(K == 1) return total;
else if((int)A.size() <= K) return max_element;
//블록을 어떤 값으로 만들었을 때, minimum large sum이 만들어지는지 찾아야 한다
int left = max_element;
int right = total;
int min_large_sum = numeric_limits<int>::max();
//binary search algorithm
while(left <= right)
{
int large_sum = 0;
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
int cnt = GetBlocks(mid, large_sum, A);
if(cnt <= K)
{
right = mid - 1;
//만든 블록수(cnt)가 작다면, 공집합을 이용해서 K개의 블록을 만들면 된다
//따라서 K개의 블록으로 못 만들었어도, minimum large sum을 기록해야 한다
if(large_sum < min_large_sum) min_large_sum = large_sum;
}
else if(cnt > K)
{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return min_large_sum;
}
6. 결과
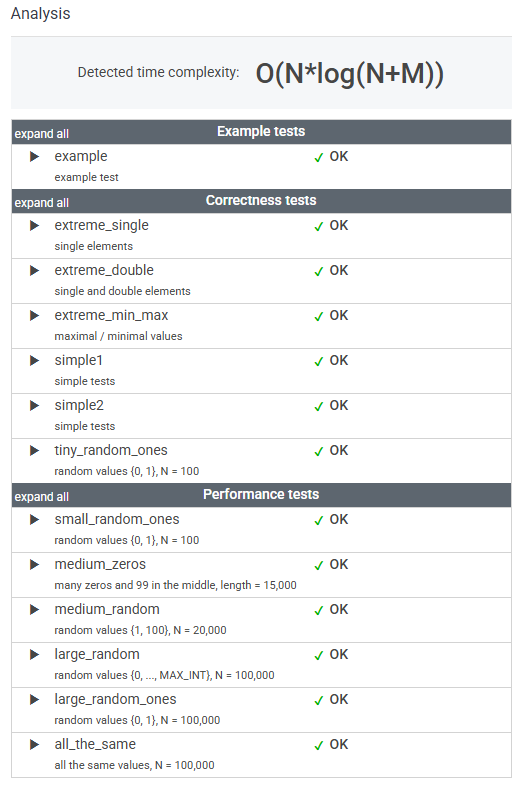
'Algorithm Problem > Codility' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lesson 14. Binary search algorithm - NailingPlanks #2 (속도 개선) (0) | 2025.03.01 |
|---|---|
| Lesson 14. Binary search algorithm - NailingPlanks #1 (0) | 2025.03.01 |
| Lesson 13. Fibonacci numbers - Ladder (0) | 2025.02.08 |
| Lesson 13. Fibonacci numbers - FibFrog #7 (속도 개선) (0) | 2025.01.27 |
| Lesson 13. Fibonacci numbers - FibFrog #6 (속도 개선) (0) | 2025.01.27 |