(밑바닥부터 만드는 컴퓨팅 시스템 2판, 인사이트(insight), 2023)을 학습하고 개인 학습용으로 정리한 내용입니다.
1. 목표 : nand2tetris/project/01에 있는 모든 칩(*.hdl)을 구현하고 시뮬레이션 해본다.
2. 일반적인 구현 팁
- 게이트마다 여려가지 방식으로 구현 가능하다. 구현은 단순할수록 좋다. 가능한 한 적은 수의 칩 파트를 사용하도록 노력해보자.
- 각 칩은 Nand 게이트만으로 구현할 수 있지만, 이미 구현된 조합 게이트를 활용하기를 추천한다.
- 이 장에서 나온 순서대로 칩을 구현하자
- Nand 게이트는 기본으로 제공된다고 가정한다. 즉, 별도 구현없이 hdl에서 바로 사용할 수 있다. (HDL 참조)
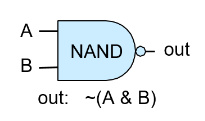
| A | B | Nand(A, B) |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
3. 논리 게이트 구현
- Not.hdl
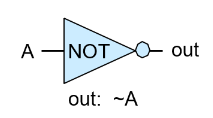
| A | Not(A) |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Nand 게이트의 입력값이 동일할 때, Not이 된다. (참조 : [Chapter 1] Nand의 표현력, 보조 정리 3)
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Not.hdl
/**
* Not gate:
* out = ((in == 0), 1, 0)
*/
CHIP Not {
IN in;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Nand(a=in, b=in, out=out);
}
- And.hdl
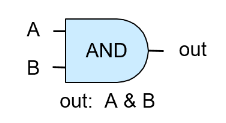
| A | B | And(A, B) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Nand 게이트의 입력값이 동일할 때, Not을 더하면 And가 된다. (참조 : [Chapter 1] Nand의 표현력, 보조 정리 3)
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/And.hdl
/**
* And gate:
* out = (((a == 1) && (b == 1))), 1, 0)
*/
CHIP And {
IN a, b;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Nand(a=a, b=b, out=v);
Not(in=v, out=out);
}
- Or.hdl
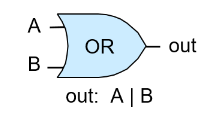
| A | B | Or(A, B) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Or는 And 와 Not으로 표현할 수 있다. (참조 : [Chapter 1] Nand의 표현력, 보조 정리 2)
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Or.hdl
/**
* Or gate:
* out = (((a == 1) || (b == 1))), 1, 0)
*/
CHIP Or {
IN a, b;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Not(in=a, out=va);
Not(in=b, out=vb);
And(a=va, b=vb, out=ab);
Not(in=ab, out=out);
}
- Xor.hdl
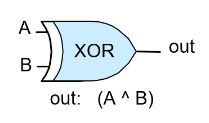
| A | B | Xor(A, B) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
모든 불 함수는 And, Or, Not만으로 표현이 가능하다. (참조 : [Chapter 1] Nand의 표현력, 보조 정리 1)
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Xor.hdl
/**
* Exclusive-or gate:
* out = (((a == 0) & (b = 1)) | ((a == 1) & (b = 0)), 1, 0)
*/
CHIP Xor {
IN a, b;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Not(in=a, out=va);
And(a=va, b=b, out=v1);
Not(in=b, out=vb);
And(a=a, b=vb, out=v2);
Or(a=v1, b=v2, out=out);
}
- Mux.hdl
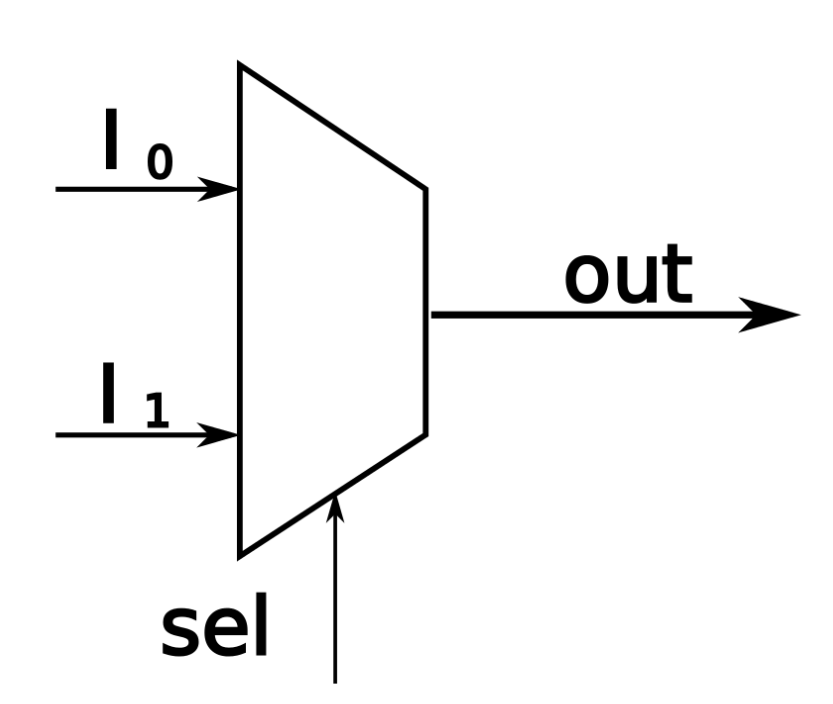
| a | b | sel | out |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| sel | out |
| 0 | a |
| 1 | b |
모든 불 함수는 And, Or, Not만으로 표현이 가능하다. (참조 : [Chapter 1] Nand의 표현력, 보조 정리 1)
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Mux.hdl
/**
* Multiplexor:
* out = ((sel == 0), a, b)
*/
CHIP Mux {
IN a, b, sel;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Not(in=sel, out=ns);
And(a=a, b=ns, out=v1);
And(a=sel, b=b, out=v2);
Or(a=v1, b=v2, out=out);
}
- DMux.hdl
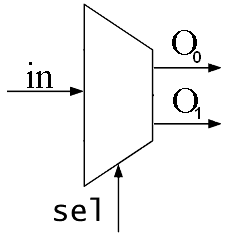
| sel | (a, b) | |
| 0 | (in, 0) | |
| 1 | (0, in) | |
sel이 0일 때, 입력 값을 출력 a로 연결(out=a)하는 게이트와
sel이 1일 때, 입력 값을 출력 b로 연결(out=b)하는 게이트가 있어야 한다.
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/DMux.hdl
/**
* Demultiplexor:
* [a, b] = ((sel == 0), [in, 0], [0, in])
*/
CHIP DMux {
IN in, sel;
OUT a, b;
PARTS:
Not(in=sel, out=ns);
And(a=in, b=ns, out=a);
And(a=sel, b=in, out=b);
}
- Not16.hdl
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Not16.hdl
/**
* 16-bit Not gate:
* out[i] = ((in[i] == 0), 1, 0) for i = 0..15
*/
CHIP Not16 {
IN in[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
Nand(a=in[0], b=in[0], out=out[0]);
Nand(a=in[1], b=in[1], out=out[1]);
Nand(a=in[2], b=in[2], out=out[2]);
Nand(a=in[3], b=in[3], out=out[3]);
Nand(a=in[4], b=in[4], out=out[4]);
Nand(a=in[5], b=in[5], out=out[5]);
Nand(a=in[6], b=in[6], out=out[6]);
Nand(a=in[7], b=in[7], out=out[7]);
Nand(a=in[8], b=in[8], out=out[8]);
Nand(a=in[9], b=in[9], out=out[9]);
Nand(a=in[10], b=in[10], out=out[10]);
Nand(a=in[11], b=in[11], out=out[11]);
Nand(a=in[12], b=in[12], out=out[12]);
Nand(a=in[13], b=in[13], out=out[13]);
Nand(a=in[14], b=in[14], out=out[14]);
Nand(a=in[15], b=in[15], out=out[15]);
}
- And16.hdl
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/And16.hdl
/**
* 16-bit bitwise And gate:
* out[i] = And(a[i],b[i]) for i = 0..15
*/
CHIP And16 {
IN a[16], b[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
Nand(a=a[0], b=b[0], out=v0);
Not(in=v0, out=out[0]);
Nand(a=a[1], b=b[1], out=v1);
Not(in=v1, out=out[1]);
Nand(a=a[2], b=b[2], out=v2);
Not(in=v2, out=out[2]);
Nand(a=a[3], b=b[3], out=v3);
Not(in=v3, out=out[3]);
Nand(a=a[4], b=b[4], out=v4);
Not(in=v4, out=out[4]);
Nand(a=a[5], b=b[5], out=v5);
Not(in=v5, out=out[5]);
Nand(a=a[6], b=b[6], out=v6);
Not(in=v6, out=out[6]);
Nand(a=a[7], b=b[7], out=v7);
Not(in=v7, out=out[7]);
Nand(a=a[8], b=b[8], out=v8);
Not(in=v8, out=out[8]);
Nand(a=a[9], b=b[9], out=v9);
Not(in=v9, out=out[9]);
Nand(a=a[10], b=b[10], out=v10);
Not(in=v10, out=out[10]);
Nand(a=a[11], b=b[11], out=v11);
Not(in=v11, out=out[11]);
Nand(a=a[12], b=b[12], out=v12);
Not(in=v12, out=out[12]);
Nand(a=a[13], b=b[13], out=v13);
Not(in=v13, out=out[13]);
Nand(a=a[14], b=b[14], out=v14);
Not(in=v14, out=out[14]);
Nand(a=a[15], b=b[15], out=v15);
Not(in=v15, out=out[15]);
}
- Or16.hdl
게이트 순서는 편집하기 편한 순서로 나열했다.
16비트 게이트를 작성해보니, Or 게이트 기본 설계가 비효율적인가? 의구심이 든다.
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Or16.hdl
/**
* 16-bit bitwise Or gate:
* out[i] = (a[i] Or b[i]) for i = 0..15
*/
CHIP Or16 {
IN a[16], b[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
Not(in=a[0], out=a0);
Not(in=a[1], out=a1);
Not(in=a[2], out=a2);
Not(in=a[3], out=a3);
Not(in=a[4], out=a4);
Not(in=a[5], out=a5);
Not(in=a[6], out=a6);
Not(in=a[7], out=a7);
Not(in=a[8], out=a8);
Not(in=a[9], out=a9);
Not(in=a[10], out=a10);
Not(in=a[11], out=a11);
Not(in=a[12], out=a12);
Not(in=a[13], out=a13);
Not(in=a[14], out=a14);
Not(in=a[15], out=a15);
Not(in=b[0], out=b0);
Not(in=b[1], out=b1);
Not(in=b[2], out=b2);
Not(in=b[3], out=b3);
Not(in=b[4], out=b4);
Not(in=b[5], out=b5);
Not(in=b[6], out=b6);
Not(in=b[7], out=b7);
Not(in=b[8], out=b8);
Not(in=b[9], out=b9);
Not(in=b[10], out=b10);
Not(in=b[11], out=b11);
Not(in=b[12], out=b12);
Not(in=b[13], out=b13);
Not(in=b[14], out=b14);
Not(in=b[15], out=b15);
And(a=a0, b=b0, out=ab0);
And(a=a1, b=b1, out=ab1);
And(a=a2, b=b2, out=ab2);
And(a=a3, b=b3, out=ab3);
And(a=a4, b=b4, out=ab4);
And(a=a5, b=b5, out=ab5);
And(a=a6, b=b6, out=ab6);
And(a=a7, b=b7, out=ab7);
And(a=a8, b=b8, out=ab8);
And(a=a9, b=b9, out=ab9);
And(a=a10, b=b10, out=ab10);
And(a=a11, b=b11, out=ab11);
And(a=a12, b=b12, out=ab12);
And(a=a13, b=b13, out=ab13);
And(a=a14, b=b14, out=ab14);
And(a=a15, b=b15, out=ab15);
Not(in=ab0, out=out[0]);
Not(in=ab1, out=out[1]);
Not(in=ab2, out=out[2]);
Not(in=ab3, out=out[3]);
Not(in=ab4, out=out[4]);
Not(in=ab5, out=out[5]);
Not(in=ab6, out=out[6]);
Not(in=ab7, out=out[7]);
Not(in=ab8, out=out[8]);
Not(in=ab9, out=out[9]);
Not(in=ab10, out=out[10]);
Not(in=ab11, out=out[11]);
Not(in=ab12, out=out[12]);
Not(in=ab13, out=out[13]);
Not(in=ab14, out=out[14]);
Not(in=ab15, out=out[15]);
}
- Mux16.hdl
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Mux16.hdl
/**
* 16-bit multiplexor:
* out[i] = ((sel == 0), a[i], b[i]) for i = 0..15
*/
CHIP Mux16 {
IN a[16], b[16], sel;
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
Not(in=sel, out=ns);
And(a=a[0], b=ns, out=a0);
And(a=a[1], b=ns, out=a1);
And(a=a[2], b=ns, out=a2);
And(a=a[3], b=ns, out=a3);
And(a=a[4], b=ns, out=a4);
And(a=a[5], b=ns, out=a5);
And(a=a[6], b=ns, out=a6);
And(a=a[7], b=ns, out=a7);
And(a=a[8], b=ns, out=a8);
And(a=a[9], b=ns, out=a9);
And(a=a[10], b=ns, out=a10);
And(a=a[11], b=ns, out=a11);
And(a=a[12], b=ns, out=a12);
And(a=a[13], b=ns, out=a13);
And(a=a[14], b=ns, out=a14);
And(a=a[15], b=ns, out=a15);
And(a=sel, b=b[0], out=b0);
And(a=sel, b=b[1], out=b1);
And(a=sel, b=b[2], out=b2);
And(a=sel, b=b[3], out=b3);
And(a=sel, b=b[4], out=b4);
And(a=sel, b=b[5], out=b5);
And(a=sel, b=b[6], out=b6);
And(a=sel, b=b[7], out=b7);
And(a=sel, b=b[8], out=b8);
And(a=sel, b=b[9], out=b9);
And(a=sel, b=b[10], out=b10);
And(a=sel, b=b[11], out=b11);
And(a=sel, b=b[12], out=b12);
And(a=sel, b=b[13], out=b13);
And(a=sel, b=b[14], out=b14);
And(a=sel, b=b[15], out=b15);
Or(a=a0, b=b0, out=out[0]);
Or(a=a1, b=b1, out=out[1]);
Or(a=a2, b=b2, out=out[2]);
Or(a=a3, b=b3, out=out[3]);
Or(a=a4, b=b4, out=out[4]);
Or(a=a5, b=b5, out=out[5]);
Or(a=a6, b=b6, out=out[6]);
Or(a=a7, b=b7, out=out[7]);
Or(a=a8, b=b8, out=out[8]);
Or(a=a9, b=b9, out=out[9]);
Or(a=a10, b=b10, out=out[10]);
Or(a=a11, b=b11, out=out[11]);
Or(a=a12, b=b12, out=out[12]);
Or(a=a13, b=b13, out=out[13]);
Or(a=a14, b=b14, out=out[14]);
Or(a=a15, b=b15, out=out[15]);
}
- Or8Way.hdl
8입력, 1-bit 출력
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Or8Way.hdl
/**
* 8-way Or gate:
* out = in[0] Or in[1] Or ... Or in[7]
*/
CHIP Or8Way {
IN in[8];
OUT out;
PARTS:
Or(a=in[0], b=in[1], out=v1);
Or(a=v1, b=in[2], out=v2);
Or(a=v2, b=in[3], out=v3);
Or(a=v3, b=in[4], out=v4);
Or(a=v4, b=in[5], out=v5);
Or(a=v5, b=in[7], out=out);
}
- Mux4Way16.hdl
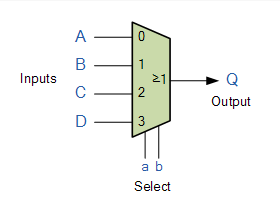
| sel[1] | sel[0] | out |
| 0 | 0 | a |
| 0 | 1 | b |
| 1 | 0 | c |
| 1 | 1 | d |
4-입력, 16-bit 출력
Mux16을 이용해야 한다.
sel-bit 진리표에서 규칙을 찾아야 한다.
'00 → a'도 규칙이지만, 이것은 out이 a,b,c,d로 각각 결정되는 너무 세부적인 규칙이다. ab, cd와 같이 두개 이상씩 묶을 수 있는 규칙을 찾아보자.
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Mux4Way16.hdl
/**
* 4-way 16-bit multiplexor:
* out = a if sel == 00
* b if sel == 01
* c if sel == 10
* d if sel == 11
*/
CHIP Mux4Way16 {
IN a[16], b[16], c[16], d[16], sel[2];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
Mux16(a=a, b=c, sel=sel[1], out=r1);
Mux16(a=b, b=d, sel=sel[1], out=r2);
Mux16(a=r1, b=r2, sel=sel[0], out=out);
}
- Mux8Way16.hdl
| sel[2] | sel[1] | sel[0] | out |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | a |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | b |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | c |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | d |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | e |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | f |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | g |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | h |
Mux4Way16 때와 같이, 크게 묶을 수 있는 규칙을 찾아야 한다.
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/Mux8Way16.hdl
/**
* 8-way 16-bit multiplexor:
* out = a if sel == 000
* b if sel == 001
* ...
* h if sel == 111
*/
CHIP Mux8Way16 {
IN a[16], b[16], c[16], d[16],
e[16], f[16], g[16], h[16],
sel[3];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
Mux16(a=a, b=c, sel=sel[1], out=ac);
Mux16(a=b, b=d, sel=sel[1], out=bd);
Mux16(a=e, b=g, sel=sel[1], out=eg);
Mux16(a=f, b=h, sel=sel[1], out=fh);
Mux16(a=ac, b=bd, sel=sel[0], out=r1);
Mux16(a=eg, b=fh, sel=sel[0], out=r2);
Mux16(a=r1, b=r2, sel=sel[2], out=out);
}
- DMux4Way.hdl

Mux4Way16, Mux8Way16 때와 같이, 크게 묶을 수 있는 규칙을 찾아야 한다.
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/DMux4Way.hdl
/**
* 4-way demultiplexor:
* [a, b, c, d] = [in, 0, 0, 0] if sel == 00
* [0, in, 0, 0] if sel == 01
* [0, 0, in, 0] if sel == 10
* [0, 0, 0, in] if sel == 11
*/
CHIP DMux4Way {
IN in, sel[2];
OUT a, b, c, d;
PARTS:
DMux(in=in, sel=sel[1], a=ab, b=cd);
DMux(in=ab, sel=sel[0], a=a, b=b);
DMux(in=cd, sel=sel[0], a=c, b=d);
}
- DMux8Way.hdl
| sel[2] | sel[1] | sel[0] | out |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | a |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | b |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | c |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | d |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | e |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | f |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | g |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | h |
Mux4Way16, Mux8Way16, DMux4Way 때와 같이, 크게 묶을 수 있는 규칙을 찾아야 한다.
// This file is part of http://www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/01/DMux8Way.hdl
/**
* 8-way demultiplexor:
* [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h] = [in, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] if sel == 000
* [0, in, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] if sel == 001
* ...
* [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, in] if sel == 111
*/
CHIP DMux8Way {
IN in, sel[3];
OUT a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h;
PARTS:
DMux(in=in, sel=sel[2], a=abcd, b=efgh);
DMux(in=abcd, sel=sel[1], a=ab, b=cd);
DMux(in=efgh, sel=sel[1], a=ef, b=gh);
DMux(in=ab, sel=sel[0], a=a, b=b);
DMux(in=cd, sel=sel[0], a=c, b=d);
DMux(in=ef, sel=sel[0], a=e, b=f);
DMux(in=gh, sel=sel[0], a=g, b=h);
}
'밑바닥부터 만드는 컴퓨팅 시스템 (Nand to Tetris)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Chapter 2] 가산기 (0) | 2024.02.09 |
|---|---|
| [Chapter 2] 불 연산 (Boolean Arithmetic) (0) | 2024.02.09 |
| [Chapter 1] HDL 문법 (0) | 2024.02.09 |
| [Chapter 1] HDL (Hardware Description Language) (0) | 2024.02.04 |
| [Chapter 1] 논리 게이트 (0) | 2024.02.04 |