반응형
1. 문제
A prime is a positive integer X that has exactly two distinct divisors: 1 and X. The first few prime integers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 and 13.
A semiprime is a natural number that is the product of two (not necessarily distinct) prime numbers. The first few semiprimes are 4, 6, 9, 10, 14, 15, 21, 22, 25, 26.
You are given two non-empty arrays P and Q, each consisting of M integers. These arrays represent queries about the number of semiprimes within specified ranges.
Query K requires you to find the number of semiprimes within the range (P[K], Q[K]), where 1 ≤ P[K] ≤ Q[K] ≤ N.
For example, consider an integer N = 26 and arrays P, Q such that:
P[0] = 1 Q[0] = 26
P[1] = 4 Q[1] = 10
P[2] = 16 Q[2] = 20
The number of semiprimes within each of these ranges is as follows:
- (1, 26) is 10,
- (4, 10) is 4,
- (16, 20) is 0.
Write a function:
vector<int> solution(int N, vector<int> &P, vector<int> &Q);
that, given an integer N and two non-empty arrays P and Q consisting of M integers, returns an array consisting of M elements specifying the consecutive answers to all the queries.
For example, given an integer N = 26 and arrays P, Q such that:
P[0] = 1 Q[0] = 26
P[1] = 4 Q[1] = 10
P[2] = 16 Q[2] = 20
the function should return the values [10, 4, 0], as explained above.
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
- N is an integer within the range [1..50,000];
- M is an integer within the range [1..30,000];
- each element of arrays P and Q is an integer within the range [1..N];
- P[i] ≤ Q[i].
주어진 범위[P...Q]에서 SemiPrime 개수를 세는 문제
Prime Number(소수): 1 과 자기자신을 약수로 가지는 양의 정수 (예: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13)
SemiPrime: 두 개의 소수(같은 수도 가능)의 곱으로 이루어진 자연수 (예: 4, 6, 9, 10, 14, 15, 21, 22, 25, 26)
예시) return [10, 4, 0]
N = 26
| P[0] | 1 | Q[0] | 26 |
| P[1] | 4 | Q[1] | 10 |
| P[2] | 16 | Q[2] | 20 |
P[0] ~ Q[0] SemiPrime 개수: 10, (4, 6, 9, 10, 14, 15, 21, 22, 25, 26)
P[1] ~ Q[1] SemiPrime 개수: 4, (4, 6, 9, 10)
P[0] ~ Q[2] SemiPrime 개수: 0
2. 매개변수 제한
- N: 1 ~ 50,000
- P, Q 크기: 1 ~ 30,000
- P, Q 요소 값 범위: 1 ~ N
- \( P[K] \leq Q[K] \)
3. 문제풀이 전략
- N까지 소수를 구한다 (소수 판별 알고리즘)
- 구해진 소수들을 이용해서 SemiPrime을 구한다
- [P...Q] 범위안에 있는 SemiPrime 개수를 센다
4. 코드
#include <algorithm>
vector<int> solution(int N, vector<int> &P, vector<int> &Q) {
//prime number 구하기
vector<int> primes = {};
primes.emplace_back(2);
for(int i = 3; i <= N; i++)
{
if(i % 2 == 0) continue;
bool prime_num = true;
for(int j = 2; j * j <= i; j++) // j <= sqrt(i)
{
if(i % j == 0)
{
prime_num = false;
break;
}
}
if(prime_num) primes.emplace_back(i);
}
//semi prime number 구하기
vector<int> semi_primes = {};
for(size_t i = 0; i < primes.size(); i++)
{
bool stop = false;
for(size_t j = i; j < primes.size(); j++)
{
int temp = primes[i] * primes[j];
if(temp > N)
{
if(i == j) stop = true;
break;
}
semi_primes.emplace_back(temp);
}
if(stop) break;
}
sort(semi_primes.begin(), semi_primes.end());
//[P..Q] 범위안에 있는 semi prime number 개수 세기
vector<int> result = {};
for(size_t K = 0; K < P.size(); K++)
{
int cnt = 0;
for(size_t i = 0; i < semi_primes.size(); i++)
{
if(semi_primes[i] > Q[K]) break;
if(P[K] <= semi_primes[i] && semi_primes[i] <= Q[K]) cnt++;
}
result.emplace_back(cnt);
}
return result;
}
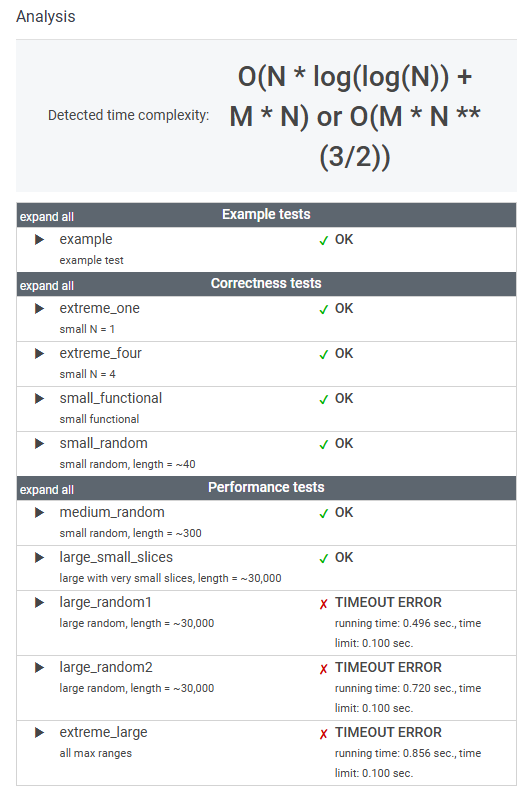
5. 결과
반응형
'Algorithm Problem > Codility' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lesson 11. Sieve of Eratosthenes - CountSemiPrimes #3 (속도 개선-2) (0) | 2025.01.03 |
|---|---|
| Lesson 11. Sieve of Eratosthenes - CountSemiPrimes #2 (속도 개선-1) (0) | 2025.01.02 |
| Lesson 11. Sieve of Eratosthenes - CountNonDivisible #2 (속도 개선) (1) | 2024.12.29 |
| Lesson 11. Sieve of Eratosthenes - CountNonDivisible #1 (0) | 2024.12.29 |
| Lesson 10. Prime and composite numbers - Peaks #3 (속도 개선-2) (0) | 2024.12.28 |