Game Programming in C++ Chapter1 - 공 움직이기

책의 소스 코드를 직접 작성해보면서 정리한 글입니다. (실습환경: windows)
책 소스 코드: GitHub - gameprogcpp/code: Game Programming in C++ Code
1. 공(ball)의 움직임
공을 움직이기 위해서는 공의 위치, 공의 속도(속력과 방향), 충돌감지 코드가 필요하다.
2. 공의 위치
공의 위치는 공을 그릴 때, 사용했다.
struct Vector2
{
float x, y;
};
3. 공의 방향
공은 x, y 방향으로 모두 이동한다.
공의 방향은 Vector2 자료구조를 이용해서 구현할 수 있다.
| + | - | |
| x | 오른쪽으로 이동중 | 왼쪽으로 이동중 |
| y | 아래로 이동중 | 위로 이동중 |
4. 충돌감지
공은 paddle 혹은 wall에 충돌할 수 있다. 둘 다, 공의 방향을 바꿔주면 된다.
단, paddle의 경우, 충돌하지 못했을 때, game over 등 다른 처리가 필요하다.
● wall 충돌 감지


● paddle 충돌 감지
a. |paddle.y - ball.y| paddle 높이보다 작아야 한다.
paddle.y 는 paddle의 중심 좌표이기 때문에,
정확히는 |paddle.y - ball.y| 값이 \( \text{paddle height} \div 2 \) 보다 작아야 한다.

b. ball이 paddle 방향으로 움직이고 있어야 한다.
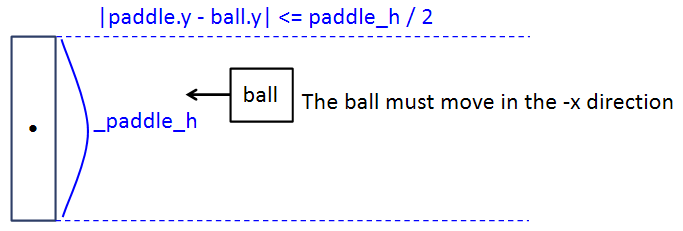
c. ball.x가 적절한(paddle.x와 충돌하는) 값을 가지고 있어야 한다.
a, b, c 조건을 코드로 구현하면 다음과 같다.
float diff = _paddle_pos.y - _ball_pos.y;
diff = (diff > 0.0f) ? diff : (diff * -1);
if (
// Our y-difference is small enough
diff <= (_paddle_h / 2.0f) &&
// We are in the correct x-position
((20.0f <= _ball_pos.x) && (_ball_pos.x <= 25.0f)) &&
// The ball is moving to the left
_ball_velicity.x < 0.0f
)
{
_ball_velicity.x *= -1.0f;
}
5. Game.hpp
공 방향 변수를 추가한다.
#include "SDL3/SDL.h"
struct Vector2
{
float x, y;
};
class Game
{
public:
...(생략)...
private:
...(생략)...
Vector2 _ball_velicity; // ball 방향
};
6. Game.cpp
● initialize() 수정
_ball_velicity 변수를 초기화 한다.
bool Game::initialize(int w, int h)
{
...(생략)...
_ball_velicity.x = -200.0f;
_ball_velicity.y = 235.0f;
return true;
}
● updateGame() 수정
공의 이동, 충돌감지 코드를 추가했다.
void Game::updateGame()
{
Uint64 current_time = SDL_GetTicks();
while (current_time < _ticks_cnt + 16) //16ms
{
current_time = SDL_GetTicks();
}
//delta time = last frame - current frame
//converting to per second
float delta_time = (SDL_GetTicks() - _ticks_cnt) / 1000.0f;
//delta time validation
//maximum delta time is 0.05 second
if (delta_time > 0.05f)
{
delta_time = 0.05f;
}
_ticks_cnt = SDL_GetTicks(); // update tick count for next frame
if (_paddle_dir != 0)
{
//moving speed is 300.0f/sec
_paddle_pos.y += _paddle_dir * 300.0f * delta_time;
//if out of wall
if (_paddle_pos.y < _paddle_h / 2.0f + _thickness)
{
_paddle_pos.y = _paddle_h / 2.0f + _thickness;
}
else if (_paddle_pos.y > (static_cast<float>(_h) - _paddle_h / 2.0f - _thickness))
{
_paddle_pos.y = static_cast<float>(_h) - _paddle_h / 2.0f - _thickness;
}
}
//change in the ball position
_ball_pos.x += _ball_velicity.x * delta_time;
_ball_pos.y += _ball_velicity.y * delta_time;
//collision detection
float diff = _paddle_pos.y - _ball_pos.y;
diff = (diff > 0.0f) ? diff : (diff * -1);
if (
diff <= (_paddle_h / 2.0f) && // Our y-difference is small enough
((20.0f <= _ball_pos.x) && (_ball_pos.x <= 25.0f)) && // We are in the correct x-position
_ball_velicity.x < 0.0f // The ball is moving to the left
)
{
_ball_velicity.x *= -1.0f;
}
else if (_ball_pos.x <= 0.0f) // game over
{
//_is_running = false;
_ball_pos.x = static_cast<float>(_w) / 2.0f;
_ball_pos.y = static_cast<float>(_h) / 2.0f;
}
//collision detection with the right wall
else if ((_ball_pos.x >= (static_cast<float>(_w) - _thickness)) && (_ball_velicity.x > 0.0f))
{
_ball_velicity.x *= -1;
}
//collision detection with the top wall
if ((_ball_pos.y <= _thickness) && (_ball_velicity.y < 0.0f))
{
_ball_velicity.y *= -1;
}
//collision detection with the bottom wall
else if ((_ball_pos.y >= (static_cast<float>(_h) - _thickness)) && (_ball_velicity.y > 0.0f))
{
_ball_velicity.y *= -1;
}
}
7. 결과
